Understanding Silicone Medical Balloons and Their Main Medical Applications
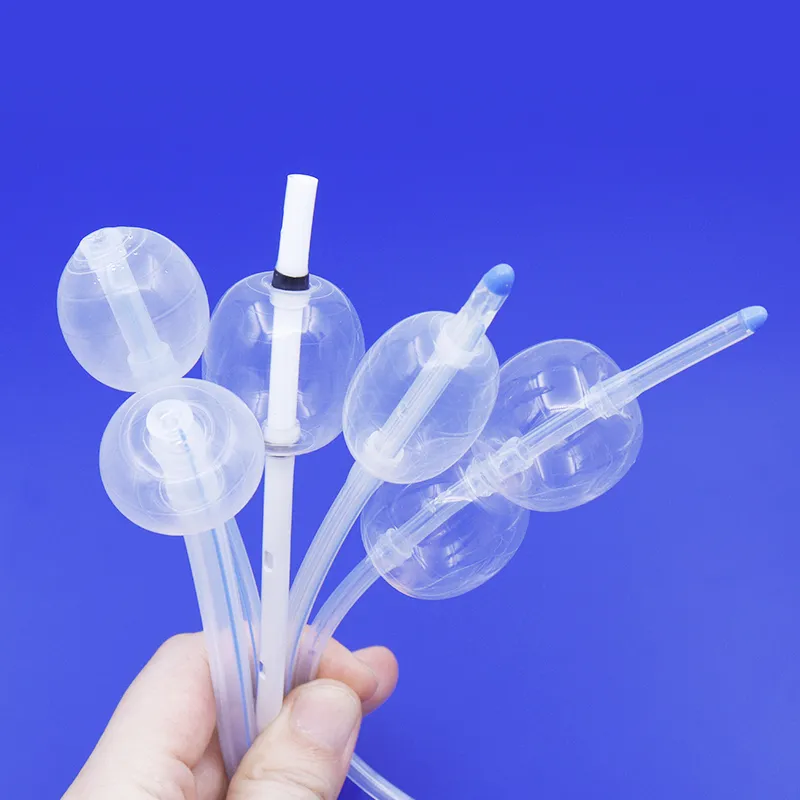

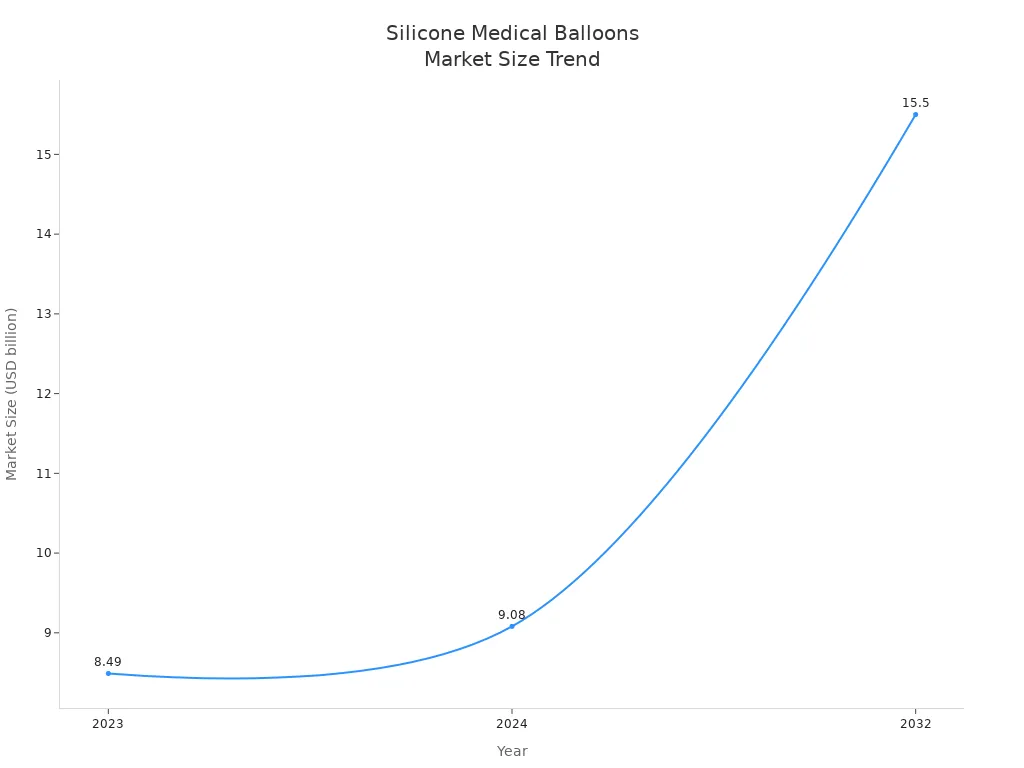
A silicone medical balloon is a soft and bendy tool. It is used in many medical treatments. Doctors use these balloons for holding things in place. They also use them for stretching, anchoring, and putting in stents. Patients feel more comfortable because silicone fits the body well. The world needs more silicone medical balloons each year. This is because people want less painful treatments. More people also have long-term illnesses now.

Key Takeaways
- Silicone medical balloons are soft and bendy tools. They help doctors hold, stretch, or support body parts. They do this in a safe and comfortable way.
- These balloons fit well inside the body. They cause less pain for patients. They also lower the chance of infection. This is because silicone is gentle and works well with the body.
- Doctors use silicone balloons in many ways. They use them for stomach treatments and urine drainage. They also use them in heart procedures and new therapies. These balloons help make patient care better.
- Silicone balloons come in many sizes and shapes. This lets doctors pick the best one for each patient and treatment.
- New designs and materials make silicone balloons strong and safe. They work well and help patients heal faster. Patients also have fewer side effects.
Basic Knowledge of Silicone Medical Balloons
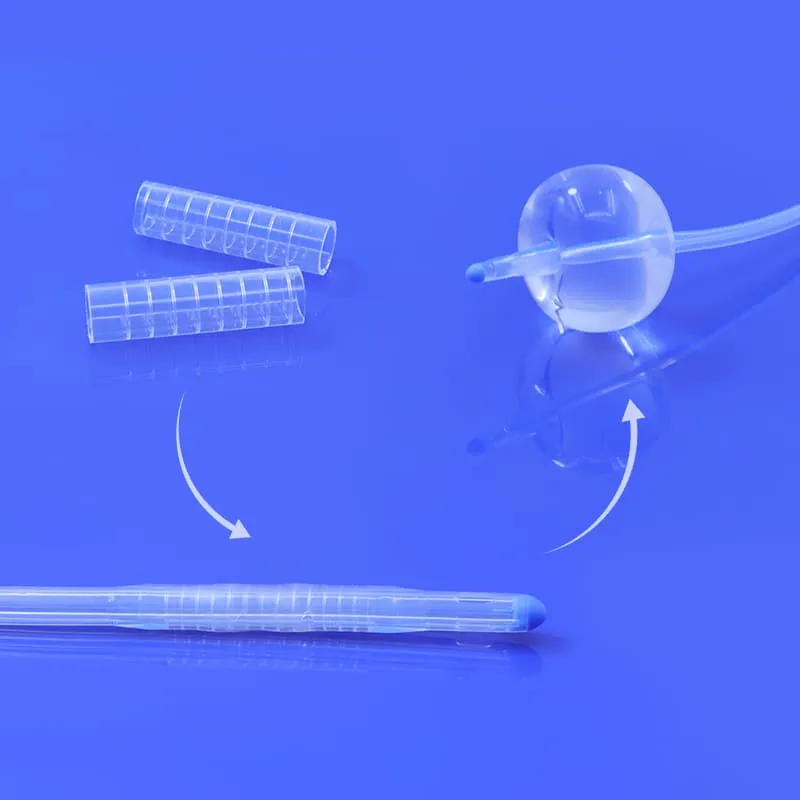
What Is a Silicone Medical Balloon
A silicone medical balloon is a bendy, inflatable tool made from special silicone. Doctors use these balloons in many treatments because they are soft and strong. They are also safe for the body. The balloon can stretch up to ten times its size and still stay strong. This lets it fit inside different body parts without hurting anything.
There are different kinds of silicone medical balloons. Each type is made for a certain job.
- Silicone-coated Foley catheters have balloons that help drain urine and keep the tube in place in the bladder.
- These balloons are smooth, so they do not bother the body much. They are good for people who cannot use latex.
- Some balloons have even shapes and strong tips. This helps stop injuries and makes the device work better.
How It Works
A silicone medical balloon works by filling up inside the body. It does jobs like holding, anchoring, or stretching tissues. The way it is made helps it do these things well.
- The balloon usually has two layers: a soft outside and a strong inside.
- The outside layer is the smallest size it needs to be and can stretch a bit.
- The inside layer makes the balloon strong and controls how much it grows.
- When a doctor fills the balloon, the outside opens first. This makes a smooth surface that holds the device in place.
- If the balloon needs to get bigger, the outside stretches a little more, but the inside keeps the shape steady.
- This helps the balloon fit many body sizes and shapes without harm.
- The balloon can then hold a device, open a blocked path, or gently stretch tissue as needed.
The special way silicone medical balloons are made makes them good for many uses. They do not break down from chemicals, heat, or being used again. This means they stay safe and work well during treatments.
Key Properties of Silicone Balloons

Biocompatibility and Comfort
Silicone is a great choice for medical balloons. It is safe for the body and gentle on tissues. Medical-grade silicone does not cause bad reactions or swelling. This helps patients feel less pain during and after treatments. Silicone is soft and bends easily, so it fits in sensitive places without hurting them. Its smooth surface makes it hard for bacteria to stick. This lowers the chance of infection.
- Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) is used because it is strong and flexible.
- LSR follows strict safety rules from the FDA, REACH, and ISO 13485.
- Special changes to silicone make blood clots less likely, which helps in heart and blood vessel care.
- Silicone medical balloons are safe for heart, urinary, and stomach treatments.
Compliance and Durability
Silicone balloons can stretch and go back to their shape. This is called compliance. It lets the balloon fit different body parts without breaking. Doctors pick balloons with the right wall thickness for each job. Thin walls stretch more, while thick walls give more control.
Silicone medical balloons are also very tough. Tests show they can be stretched and squeezed many times. They do not lose their shape or strength. This means they work well even after being used a lot. Doctors trust these balloons to be safe during important treatments.
Main Medical Uses of Silicone Balloons
Gastroenterology
Doctors use silicone medical balloons to help with stomach and gut problems. These balloons can open blocked areas and help people lose weight. When someone has a tight spot in their esophagus, doctors use a drug-coated balloon to stretch it. This works well for most people, with about 89 out of 100 getting better. People usually swallow easier after this treatment. Problems from the procedure do not happen often and are usually not serious.
For weight loss, doctors put a balloon inside the stomach. The balloon takes up space, so people feel full sooner. Brands like Silimed and ATIIP-Endogast work well for this. With the ATIIP-Endogast balloon, people can lose a lot of weight in one year. The Silimed balloon also helps people lose weight in six months.
Urology
Silicone balloons are important in urology for draining urine. Foley catheters use a balloon to keep the tube in the bladder. These catheters are made from medical-grade silicone, so they are safe for people with latex allergies. The balloon’s smooth surface makes using the catheter less painful.
- The balloon keeps the catheter from slipping out.
- Silicone catheters let urine flow better because they are wider.
- They are less likely to cause infections or get blocked.
- Doctors use them for long-term care because they do not bother the body as much as latex ones.
- People with sensitive skin or allergies do best with silicone catheters.
Silicone catheters usually have fewer germs stick to them than latex ones. Some have special coatings, like silver, to lower infection risk even more. Sometimes, the balloon does not go flat all the way, which can make it hard to take out. Rarely, the balloon can pop or leave pieces behind, which can block the tube or cause other issues.
Cardiovascular
Doctors use silicone medical balloons to treat heart and blood vessel problems. In angioplasty, the balloon opens up blocked blood vessels. The Gateway balloon has a silicone coating that helps it move easily through tight spots. The doctor fills the balloon to push away the blockage and let blood flow again. This is often done before putting in a stent to keep the vessel open.
Silicone coatings help doctors control the balloon better. This makes the treatment safer and more exact. Some studies show drug-coated balloons have fewer problems than regular ones, but both work well. For example, in one treatment, drug-coated balloons had fewer problems than regular silicone balloons. Most side effects, like swelling or bruising, are not serious.
A study with 103 patients used a silicone balloon to block an artery for a short time. Almost no one had serious problems. Only one person had trouble, and it was not from the balloon. The chance of stroke dropped to about 5% for people who passed the balloon test. No one died from the treatment. Even though these balloons cost more, they save money later by causing fewer problems.
Advanced Therapies
Silicone medical balloons help with many new treatments. Doctors use them to give medicine, freeze tissue, and do other special jobs. The balloon can grow inside the body to put medicine right where it is needed. This helps treat sickness with fewer side effects.
- Balloons help guide stents and other tools into place.
- They can put medicine into blood vessels or organs.
- In cryoablation, the balloon gets bigger to freeze and destroy bad tissue, like in some heart treatments.
- Balloons come in many shapes and sizes for different needs.
The POLARx cryoablation system uses a balloon that can change size to block a vein. This lets doctors freeze the area safely and fix heart rhythm problems. Silicone balloons also help stop bleeding and support heat or cold treatments in other body parts.
Design and Customization
Size and Shape Options
Medical balloon makers give doctors many choices in size and shape. This helps doctors pick the right balloon for each patient. Balloons can be round, long, flat, skinny at one end, or shaped like a tear. There are at least 15 shapes to choose from. If a doctor needs a special size or material, they can ask for it.
Doctors often use French sizes to match the balloon’s volume to the patient. The table below shows how much liquid fits in G-Tube balloons of different sizes:
| French Size |
Minimum Volume |
Recommended Volume |
Maximum Volume |
| 12Fr |
2ml |
2.5ml |
3ml |
| 14Fr |
3ml |
4ml |
5ml |
| 16Fr |
4ml |
6ml |
8ml |
| 18Fr |
6ml |
8ml |
10ml |
| 20Fr |
7ml |
10ml |
15ml |
| 24Fr |
7ml |
10ml |
15ml |
Procedure-Specific Features
Some balloons have special parts for certain treatments. A few have two chambers to help keep them in place. Others let doctors change the size during the procedure. These features help doctors control the balloon and keep people safe.
Other features include slippery coatings to make them easier to use. Some have colors to help doctors tell them apart. Radiopaque additives make balloons show up on scans. New ways of making balloons, like laser texturing, make them stronger and more bendy. These design choices help doctors work safely and get better results for patients.
In Conclusion

Silicone balloons are very important in medicine today. Their soft and bendy shape lets doctors help people with less pain. People also get better faster. New studies say that adjustable and double-balloon systems make patients safer and more comfortable. Better materials, like liquid silicone rubber, make balloons last longer. They also help doctors do more exact work. Some balloons now have sensors that give real-time information. These new ideas help doctors pick the best balloon for each person. This means patients are happier and treatments work better.
FAQs
What makes silicone medical balloons safe for the body?
Doctors pick silicone because it does not cause allergies. The material is soft and smooth, so it feels gentle. It does not bother the body’s tissues. Silicone also keeps bacteria away, which helps stop infections.
Can doctors reuse silicone medical balloons?
Most silicone medical balloons are only used one time. Using them again can make infections or problems more likely. Hospitals have strict rules to keep everyone safe.
How do doctors pick the right size balloon?
Doctors look at the patient’s body and the treatment needed. They use charts and tools to help choose the size. Some balloons come in many shapes and sizes for different jobs.
What problems can happen with silicone medical balloons?
Most people do not have big problems. Some may feel pain, swelling, or get a small infection. Sometimes, the balloon can break or move. Doctors watch patients closely to stop these problems.