Silicone Dilators vs Plastic Dilators: Comprehensive Comparison

Silicone dilators often stand out as the preferred choice for many patients due to their soft texture and flexibility. Comfort, safety, and effectiveness remain critical factors when selecting a dilator. Silicone dilators offer a smoother, more flexible experience, while plastic dilators provide a firmer feel. Clinical studies highlight several key factors that influence the decision between these materials:
- Comfort and smoothness
- Flexibility and ease of handling
- Reduced risk of injury
- Temperature control
- Durability and affordability
Every individual has unique needs, so consulting a healthcare provider ensures the safest and most effective selection.
Key Takeaways Between Silicone Dilators and Plastic Dilators
1. Silicone dilators are preferred for their soft texture and flexibility, providing greater comfort during use.
2. Plastic dilators offer a firmer feel, which some users may prefer for specific conditions requiring strong pressure.
3. Consulting a healthcare provider is essential to choose the right dilator based on individual needs and medical history.
4. Silicone dilators reduce the risk of bruising and irritation, making them ideal for patients with sensitive tissue.
5. Both types of dilators require proper cleaning to prevent infections; silicone can withstand boiling for sterilization, while plastic cannot.
6. Silicone dilators typically last longer than plastic ones, offering better long-term value despite a higher initial cost.
7. Using a dilator set allows for gradual progression in therapy, enhancing comfort and effectiveness.
8. Patients should prioritize comfort and safety when selecting a dilator to improve adherence to therapy and overall outcomes.
Dilators Overview
What Are Dilators
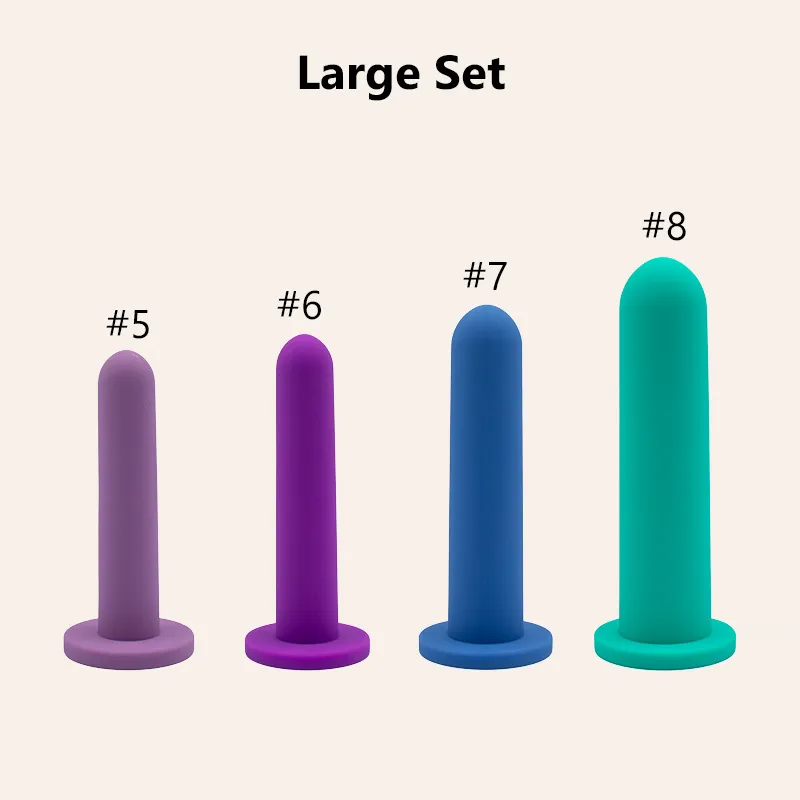
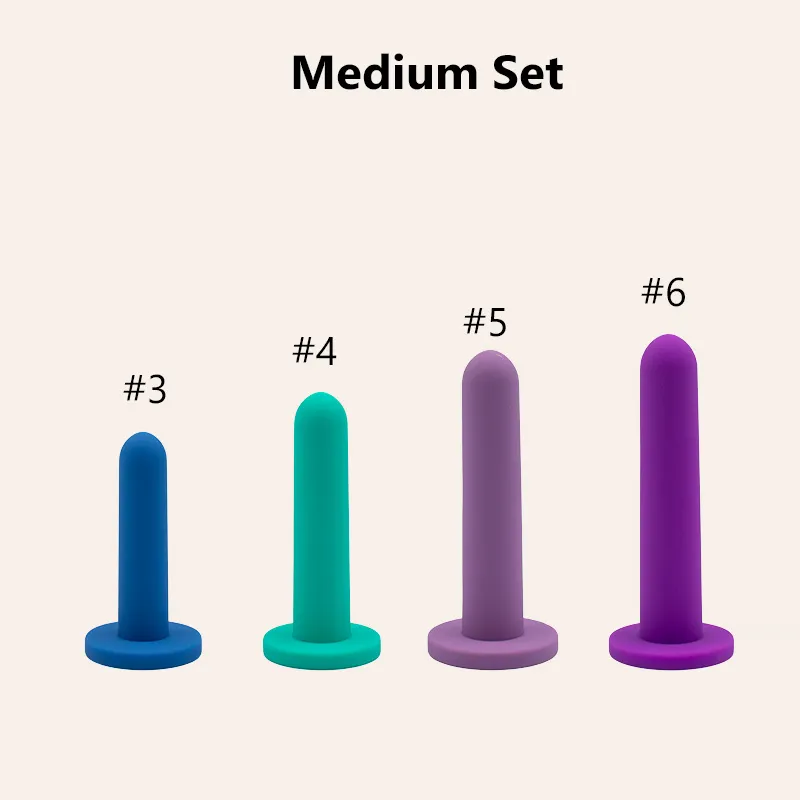
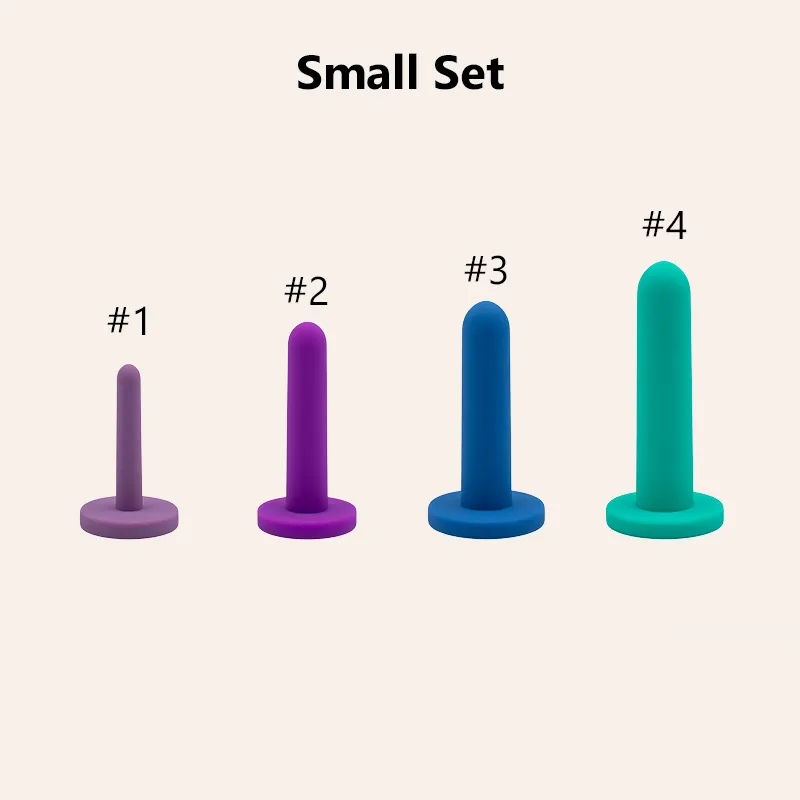
Dilators are specialized medical devices designed to gently stretch or widen body passages. Healthcare providers often recommend these tools for patients who need to improve flexibility or maintain the shape of a canal, such as the vagina or rectum. Dilators come in various sizes and materials, allowing for gradual progression and personalized treatment. Most dilators feature a smooth, tapered design that helps minimize discomfort during use. Patients can use them at home or in clinical settings under professional guidance.
Common Uses of Dilators
Medical professionals prescribe dilators for a wide range of conditions. These devices play a crucial role in both treatment and recovery. Some of the most common indications include:
- Menopause
- Vaginismus
- Dyspareunia
- Previous radiation therapy or surgery for cancer
- Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome
- Congenital conditions affecting the vagina or hymen
- Vaginal stenosis
- Reconstructive surgery
- Genito pelvic pain penetration disorder (GPPPD)
- Genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM)
- Pelvic floor hypertonus
- Lichen sclerosis
- Provoked vestibulodynia
- Vulvodynia
- Vestibulodynia
- Interstitial cystitis
- Perineal tears or episiotomy
- Painful bladder syndrome
- Pelvic pain after childbirth
- Superficial dyspareunia
- High-tone pelvic floor dysfunction
- Vaginal atrophy
- Vulvar dermatoses
- Vaginal agenesis
- Postradiation adhesions
These conditions often cause pain, tightness, or scarring. Dilators help restore normal function and improve quality of life for many patients.
Types Available
The market offers several types of dilators, each with unique features and benefits. The two main categories include mechanical and balloon dilators.
Mechanical Dilators: These devices hold the largest market share. Patients and clinicians prefer them for their durability, reusability, and precise sizing. Mechanical dilators are essential in gynecology, urology, and pelvic floor therapy.
Balloon Dilators: These tools are gaining popularity due to their minimally invasive design. Balloon dilators reduce tissue trauma and infection risk. Their use continues to grow in modern healthcare settings.
The choice between silicone and plastic dilators also affects the user experience. The table below highlights key differences in firmness and mechanism of action:
| Type of Dilator |
Firmness |
Mechanism of Action |
| Silicone Dilators |
Soft |
Less effective in stretching muscles |
| Platic Dilators |
Firm |
Stretches pelvic floor muscles better |
Selecting the right type depends on the patient's condition, comfort preferences, and treatment goals. A healthcare provider can help determine the most suitable option.
Description of Silicone Dilators
Material & Design
Silicone dilators use medical-grade silicone, a material known for its flexibility and safety. Manufacturers design these devices with a smooth, seamless surface that reduces friction during insertion. The non-porous nature of silicone prevents bacteria buildup, which supports hygiene and lowers infection risk. The following table outlines the key material properties that contribute to the flexibility and durability of silicone dilators:
| Property |
Description |
| Flexibility and Elasticity |
Maintains flexibility even at low temperatures and does not become brittle. |
| Thermal Stability |
Remains stable and retains its properties over a wide temperature range (-60°C to +250°C). |
| Chemical Resistance |
Resistant to water, oxidation, and many chemicals, making it suitable for harsh environments. |
These features make silicone dilators a reliable choice for patients who need consistent performance and safety.
Comfort & Flexibility
Patients often choose silicone dilators for their superior comfort. The soft, pliable material adapts to the body’s contours, which helps reduce pain and anxiety during use. Many users report that silicone dilators feel more natural compared to firmer alternatives. The flexible design also allows for gentle stretching, which can minimize the risk of bruising or tissue damage. The table below compares the comfort and user experience of silicone dilators with plastic dilators:
| Features |
Silicone Dilators |
Plastic Dilators |
| Comfort |
Softer, more flexible, feels more natural |
Rigid, less comfortable |
| Risk of Bruising |
Little to no bruising |
Higher risk of bruising |
| User Experience |
Encouraging for continued use |
Can feel daunting |
Clinical reports show that patients often experience discomfort with plastic dilators, which can lead to poor adherence to treatment. In contrast, silicone dilators, made from soft materials, offer greater comfort and encourage regular use.
Pros & Cons of Silicone Dilators
Silicone dilators offer several advantages, but they also have some limitations. The following list summarizes the main pros and cons:
Pros:
- Soft, flexible material enhances comfort.
- Non-porous surface supports hygiene.
- Low risk of allergic reactions.
- Suitable for sensitive users and long-term therapy.
Cons:
- May be less effective for patients who need very firm pressure.
- Can be more expensive than plastic options.
- Some users may prefer a firmer feel for certain conditions.
Silicone dilators provide a gentle, user-friendly option for many patients. They combine safety, comfort, and flexibility, making them a preferred choice in clinical practice.
Description of Plastic Dilators
Material & Design
Plastic dilators feature a rigid and inflexible construction. Manufacturers typically use medical-grade polymers to create these devices. The surface of plastic dilators feels smooth but lacks the softness found in silicone alternatives. This firmness can make insertion more challenging for some users, especially those with sensitive tissue. The design often includes a tapered tip and a uniform shaft, which helps guide the dilator into position. However, the lack of flexibility means the device does not adapt to the body's contours as easily as silicone models.
The following table highlights the primary material differences between plastic and silicone dilators:
| Features |
Plastic Dilators |
Silicone Dilators |
| Material |
Rigid and inflexible |
Soft and flexible |
| Comfort |
Level Can be uncomfortable |
More comfortable, natural |
| Pressure on Tissues |
Higher risk of bruising |
Gentle, gradual pressure |
| Temperature Control |
Inferior |
Superior |
| Durability |
Shorter lifespan |
Highly durable |
| Cleaning |
Standard cleaning |
Easy to clean |
Plastic dilators require careful handling to avoid discomfort or injury. Their rigid nature can limit their suitability for patients with pain or fragile tissue.
Firmness & Effectiveness
The firmness of plastic dilators appeals to some users who prefer a solid feel. This rigidity allows the device to maintain its shape during use, which can help stretch pelvic floor muscles more directly. However, the hard and unbending nature of plastic dilators often proves less sensitive to the delicate vaginal environment. Many patients report discomfort or even bruising after use.
- Plastic dilators offer lower cost and firm pressure, which some users find beneficial.
- The rigid design can be less sensitive to pain, making it unsuitable for individuals with fragile tissue.
- Softer silicone dilators provide a gentler force, promoting relaxation and effective stretching with less bruising.
- Consistent use of comfortable dilators, such as silicone, leads to better therapeutic outcomes.
Plastic dilators may suit individuals who require firm stretching and do not experience significant pain. Healthcare providers often recommend starting with softer materials for those with sensitivity or a history of discomfort.
Pros & Cons
Plastic dilators present several advantages and disadvantages. The following table summarizes patient feedback on key aspects:
| Aspect |
Plastic Dilators |
Silicone Dilators |
| Comfort |
Hard, can be uncomfortable |
Soft, natural feel, comfortable |
| Flexibility |
Not flexible |
Flexible, reduces injury risk |
| Temperature Control |
Limited |
Usable at various temperatures |
| Maintenance |
May require more care |
Durable, easy to clean |
Pros of Plastic Dilators:
- Lower cost compared to silicone options
- Firmness may benefit users needing strong pressure
- Available in a wide range of sizes
Cons of Plastic Dilators:
- Can cause discomfort or bruising
- Limited flexibility increases risk of injury
- Shorter lifespan and more maintenance required
Plastic dilators remain a practical choice for some patients, but many prefer silicone for greater comfort and safety. The decision depends on individual needs and medical advice.
Comfort Comparison Between Silicone and Plastic Dilators
Comfort plays a crucial role in the selection of a dilator. Many patients report that silicone dilators provide a smoother and gentler experience during therapy. The soft texture of medical-grade silicone adapts to the body's contours, which helps reduce discomfort. Plastic dilators, on the other hand, feel rigid and may cause pain or irritation, especially for individuals with sensitive tissue.
The flexible nature of silicone allows for gradual stretching, which minimizes the risk of bruising. Plastic dilators lack this flexibility and can feel harsh against delicate skin. Many women find the hardness of plastic dilators challenging, particularly during the initial stages of therapy.
User Experience: Silicone Dilators VS Plastic Dilators
Patients consistently rate their experience with silicone dilators higher than with plastic alternatives. The gentle feel of silicone reduces anxiety and encourages regular use. Individuals recovering from surgery or dealing with scar tissue often prefer silicone because it feels softer against sensitive areas.
Patients who use silicone dilators report less pain and fewer complications. The ease of handling and natural sensation contribute to a positive therapy experience. Many users continue their therapy longer and achieve better outcomes when comfort is prioritized.
Key points for user experience:
- Silicone dilators encourage consistent use due to comfort.
- Plastic dilators may discourage therapy because of discomfort.
- Soft materials help reduce anxiety and improve adherence.
Comfort remains a top priority for both patients and healthcare providers. The choice of material can significantly impact the success of therapy and overall satisfaction.
Safety Factors Between Silicone and Plastic Dilators
Allergies & Reactions
Material safety remains a top priority when selecting a dilator. Medical-grade silicone rarely causes allergic reactions. Most patients tolerate silicone well, even those with sensitive skin. Plastic dilators, made from various polymers, may contain additives or phthalates that can trigger irritation in some individuals. Healthcare providers often recommend silicone for patients with a history of allergies.
However, safety concerns extend beyond material composition. Users must follow proper hygiene practices to prevent complications. Improper use of silicone dilators can introduce bacteria, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). Inadequate cleaning before and after each session may lead to contamination and infections. Lack of proper lubrication during insertion can cause irritation and raise the risk of tearing or infection.
Risk of Bruising
The risk of bruising varies significantly between silicone and plastic dilators. Silicone dilators feature a flexible and soft design. This flexibility allows the device to adapt to the body's contours, which reduces the likelihood of bruising or irritation. The softer firmness of silicone leads to minimal bruising or discomfort, even for patients with sensitive tissue.
Plastic dilators, in contrast, have a rigid structure. The lack of flexibility increases pressure on delicate tissues. Many users report higher rates of bruising and irritation with plastic dilators, especially during the early stages of therapy. The hard surface does not yield to the body's shape, which can make insertion and stretching more uncomfortable.
Effectiveness: Silicone Dilators VS Plastic Dilators
Stretching Ability
Effectiveness remains a primary concern when selecting a dilator. Both silicone and plastic dilators aim to stretch tissues, but their material properties influence outcomes. Silicone dilators feature a soft and flexible design. This flexibility allows them to adapt to the body's natural shape, providing gentle and gradual pressure. Many users report that silicone dilators feel smoother and more comfortable. They experience less pain and bruising during therapy. The gentle approach encourages patients to continue their therapy sessions without fear or hesitation.
Plastic dilators, in contrast, have a hard and unyielding structure. This rigidity can make stretching less effective for some individuals. Users often describe plastic dilators as uncomfortable. The firm material may cause more pain and increase the risk of bruising. Some patients find it difficult to relax during therapy with plastic dilators, which can limit progress.
Suitability for Conditions
Different medical conditions require specific approaches to tissue stretching. Silicone dilators suit a wide range of patients, especially those with sensitive tissue or a history of pain. Their gentle pressure makes them ideal for individuals recovering from surgery, managing scar tissue, or dealing with conditions like vaginismus or vaginal atrophy. Healthcare providers often recommend silicone dilators for patients who need a gradual and comfortable introduction to therapy.
Plastic dilators may benefit users who require firmer pressure and do not experience significant pain. Some clinicians suggest plastic dilators for advanced stages of therapy, where increased firmness can help maintain progress. However, the risk of discomfort and bruising remains higher with plastic options.
Durability Between Silicone Dilators and Plastic Dilators
Lifespan
Durability plays a significant role in the selection of medical dilators. Silicone dilators typically last longer than plastic alternatives. Manufacturers design silicone products with medical-grade materials that resist wear and tear. The non-porous surface of silicone prevents cracks and degradation, even after repeated use and cleaning. Patients can expect silicone dilators to maintain their shape and flexibility for several years when used and cleaned properly.
Plastic dilators, on the other hand, often show signs of aging more quickly. The rigid material may develop small cracks or scratches over time. These imperfections can harbor bacteria and compromise the device’s safety. Frequent cleaning and exposure to lubricants may accelerate the breakdown of plastic. Many users report that plastic dilators lose their smoothness and structural integrity within a year of regular use.
Cost Over Time
Initial price often influences purchasing decisions, but long-term value matters more for many patients. Silicone dilators usually cost more upfront than plastic options. However, their extended lifespan means fewer replacements over time. Patients who invest in silicone dilators often save money in the long run.
Plastic dilators may seem more affordable at first. The lower price point attracts budget-conscious buyers. Yet, the need for frequent replacement increases the total cost over several years. Users may also spend more on cleaning supplies, as plastic surfaces require extra care to prevent bacterial buildup.
Ease of Use: Silicone Dilators VS Plastic Dilators
Handling
Patients often consider handling as a key factor when choosing between silicone and plastic dilators. Silicone dilators feature a soft, flexible surface that provides a secure grip, even when lubricated. This flexibility allows users to adjust the angle and pressure during insertion, which can reduce anxiety and discomfort. Many patients with limited dexterity or hand strength find silicone dilators easier to maneuver.
Plastic dilators, in contrast, have a rigid and smooth surface. This firmness can make them feel slippery, especially when users apply lubricant. Some patients report difficulty maintaining control during insertion. The lack of flexibility also means that plastic dilators do not adapt to the body's natural curves, which can increase the challenge for beginners.
Storage
Proper storage extends the life of any medical device. Silicone dilators resist temperature changes and do not warp, so users can store them in a variety of environments. Most silicone sets come with a discreet pouch or case, which protects the device from dust and bacteria. The non-porous surface of silicone also prevents odor absorption, making long-term storage simple.
Plastic dilators require more careful storage. The rigid material can crack or scratch if dropped or stored with other hard objects. Over time, plastic may absorb odors or discolor, especially if exposed to sunlight or heat. Many manufacturers recommend storing plastic dilators in a cool, dry place, away from direct light.
Silicone Dilators VS. Plastic Dilators: Which Is Better?
Pros & Cons Recap
Choosing between silicone and plastic dilators depends on several important factors. Each material offers distinct advantages and disadvantages. The following table presents a clear comparison:
| Features |
Silicone Dilators |
Plastic Dilators |
| Comfort |
Soft, flexible, natural |
Firm, rigid, less forgiving |
| Safety |
Low risk of bruising |
Higher risk of irritation |
| Hygiene |
Non-porous, easy to clean |
May retain bacteria/odors |
| Durability |
Long lifespan |
Shorter lifespan |
| Cost |
Higher upfront cost |
Lower initial cost |
| Effectiveness |
Gentle, gradual stretch |
Strong, direct pressure |
Silicone dilators provide a gentle experience. They adapt to the body's contours and reduce discomfort. Many patients report better adherence to therapy when using silicone. Plastic dilators deliver firmer pressure. Some users prefer this firmness for advanced therapy stages. However, plastic dilators often cause more bruising and require frequent replacement.
Best Choice
Healthcare providers recommend selecting a dilator based on comfort, safety, and individual therapy goals. Silicone dilators suit most patients, especially those starting therapy or managing sensitive conditions. Their soft texture and flexibility encourage regular use and minimize complications. Plastic dilators may appeal to users who need firm stretching, but these devices can increase the risk of irritation.
A simple checklist helps guide the decision:
Does the patient have sensitive tissue or pain history?
--- Choose silicone dilators.
Is firm pressure required for advanced therapy?
--- Consider plastic dilators, but monitor for discomfort.
Is long-term durability important?
--- Silicone dilators offer extended lifespan.
Is budget a primary concern?
--- Plastic dilators cost less initially, but may require frequent replacement.
Silicone and plastic dilators differ in comfort, safety, and durability. Silicone dilators provide a softer, more flexible experience. Plastic dilators offer firmness but may cause discomfort. Most healthcare professionals recommend silicone dilators for comfort and effectiveness. Each patient should review the pros and cons before making a decision. A healthcare provider can help select the best option for individual needs.