- HOME
-
PRODUCTS
High Temperature Silicone Tubing
Flexible Silicone Rubber Tubing
Large Diameter Silicone Tubing
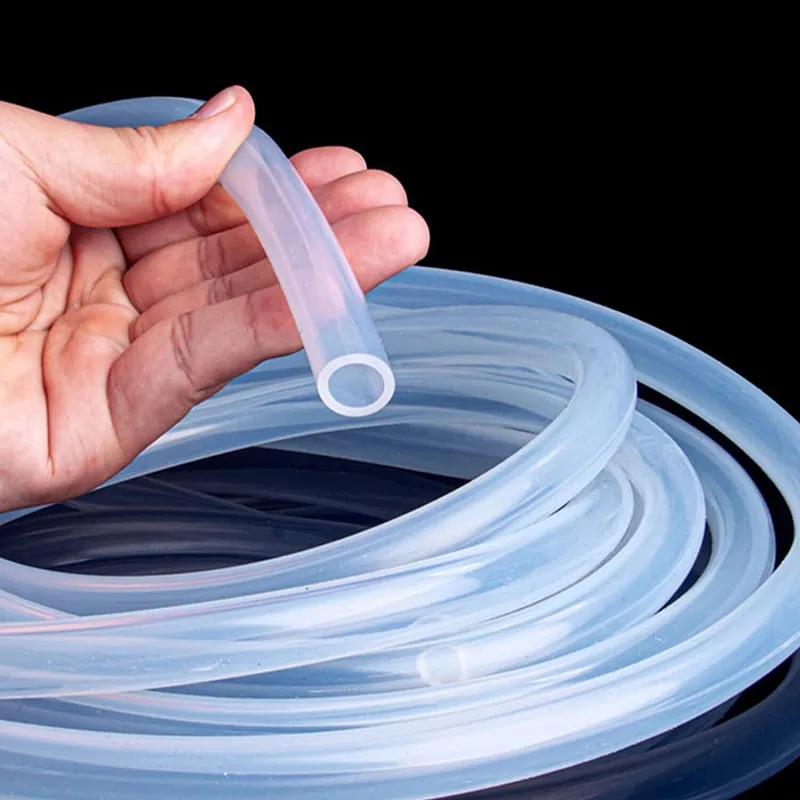










High Temp Resistant Silicone Gasket
Custom Silicone Plug for Sealing
Custom Molded Rubber and Silicone Parts
Wholesale Silicone Molded Products
Custom Silicone Rubber Products










Custom Color Silicone Foam Tubing
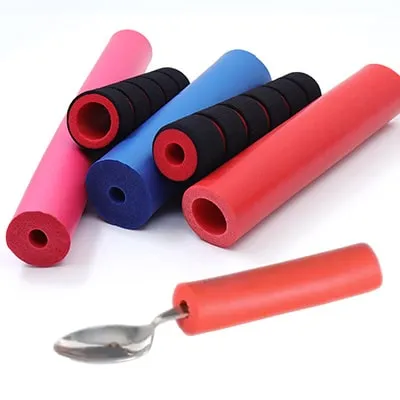
Silicone Foam Tubing for Handle Grip
Sponge Silicone Rubber Products










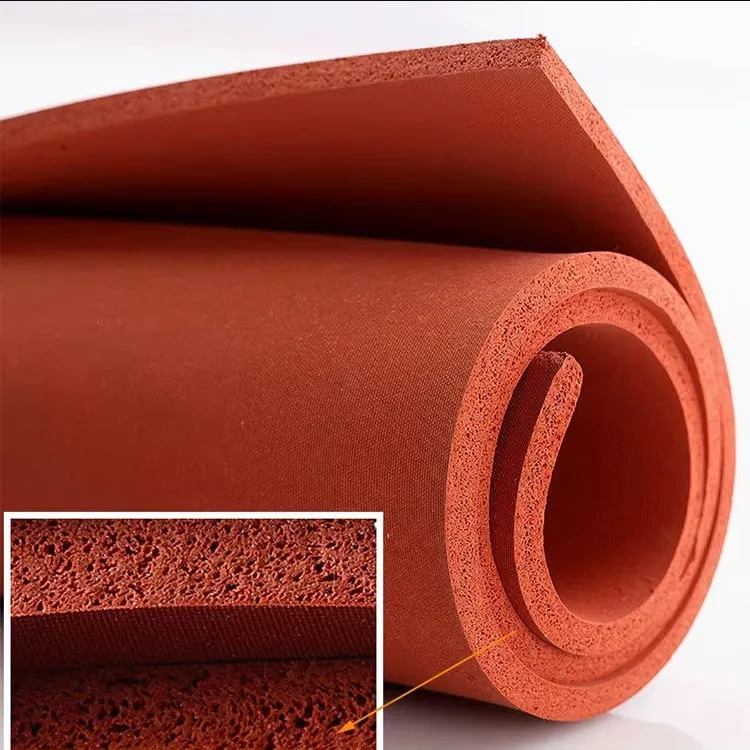
Environmental Soft Silicone Foam Sheet
High Temperature Silicone Foam Sheet
Insulating Shock-absorbing Foam Sheet
Smooth Surface Silicone Foam Sheet








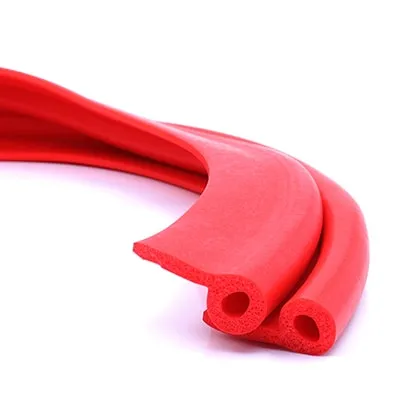
Flame Retardant Silicone Strip
Silicone Door And Window Seal Strip






- GALLERY
-
ABOUT US
Your trustworthy silicone rubber products provider.

A well-known special silicone rubber products provider that integrates the research, development, production and sales.

Authorized certifications for strict product quality control and international market entry.

Established in 2007, the 50,000sqm Jiajie Manufacturing Base owns the most advanced automatic production lines in China to reach volume production capacity up to 60tons/month, ranking the frontline in the world.

-
CUSTOMIZITION (OEM/ODM)
One-stop Service / Your satisfaction, our motivation.

Frequently asked questions about silicone products.

-
NEWS
Keep updated with Jiajie about the latest silicone products, technologies and industry trends.

Acquire useful and popular knowledge regarding the silicone industry.

- Request for Quote